Prerequisite Features
ProPrerequisites is available on Pro and Enterprise plans.
Prerequisite features allow you to control the state of other features, rules, and experiments based on the state of a prerequisite feature.
Some common use cases include:
- Grouping multiple related features under a single release feature (ex:
release-2.8) and toggling them all at once - Creating a hierarchy of features which depend on each other and safely enabling them in the correct order, per environment
- Only enabling a set of features if the user would be bucketed into "variant 1" of an experiment if exposed to that experiment
There are two types of prerequisite features in GrowthBook: Top-level Prerequisites (feature gating) and Inline Prerequisite Targeting (rule-level and experiment-level gating).
Top-Level Prerequisites
Top-level prerequisites are defined per dependent feature. They function similarly to a feature's kill switches: if the prerequisite feature is not serving true then the dependent feature will not be enabled.
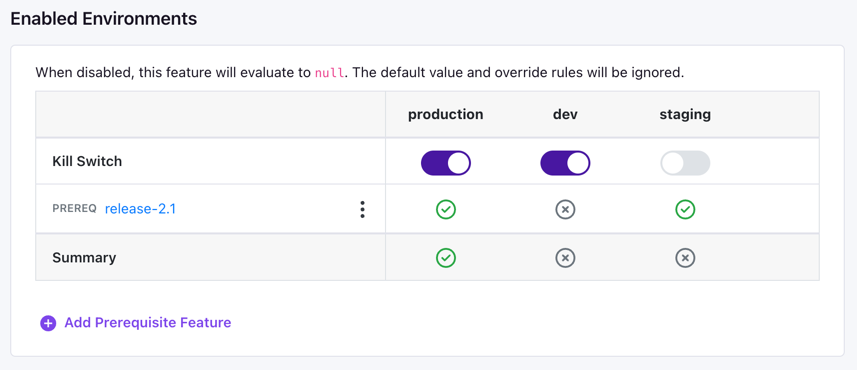
Add one or more top-level prerequisites by clicking the "Add Prerequisite Feature" button on the feature page and then selecting the feature you want to use as a prerequisite.
In order for a feature to be eligible to be a top-level prerequisite, it must be a boolean (true/false). Also, it must be in the same project as the dependent feature.
Prerequisite states and values
A summary of the prerequisite state and value will show while adding or editing a prerequisite, as well as on the dependent feature page.
- Deterministic states (live and not live) are applied to your features within GrowthBook.
- Live prerequisites which are serving
truewill allow their dependent features to be enabled - Live prerequisites which are serving
falsewill still block their dependent features (false≠true) - Not live prerequisites will always block their dependent features (they evaluate to
null, andnull≠true)
- Live prerequisites which are serving
Prerequisites with deterministic states work "out of the box" regardless of SDK version support.
Any feature that is always "not live" will not be seen by the SDK. Any feature that is always "live" will no longer reference its prerequisites in the SDK. This means that no SDK-level evaluation of prerequisites is needed (these prerequisites work irrespective of SDK version support).
- Schrödinger state means that the prerequisite's state cannot be determined in advance. It may depend on user attributes or other non-deterministic factors. (This is homage to the physicist Erwin Schrödinger who proposed a thought experiment involving a cat in a box that is both alive and dead at the same time.)
Prerequisites with a Schrödinger state must be evaluated at runtime in the SDK. Prerequisite evaluation is currently supported in the following SDK versions:
- JavaScript:
0.34.0+ - React:
0.24.0+ - Python:
1.1.0+ - C#:
1.1.0+ - Golang:
0.2.0+ - Java:
0.9.7+ - Kotlin:
1.1.60+ - Swift:
1.0.56+ - Ruby:
1.3.0+
Inline Prerequisite Targeting
Inline prerequisite targeting allows finer-grained control over prerequisite behavior than top-level prerequisites.
- Inline prerequisites can be applied at a feature's rule level, and can be environment-specific. This comes with the added benefits of feature draft releases and approvals.
- Inline prerequisites can be applied to individual experiments which may not be linked to a specific feature (such as visual experiments).
- Inline prerequisite targeting is not limited to boolean features. You can specify any evaluation condition you'd like (ex: prerequisite value is: greater than 3, in a list of allowed values, or matches a regex pattern). You can even do advanced targeting with JSON.
EnterprisePrerequisite Targeting is available on Enterprise plans.
To create an inline prerequisite within a feature, simply add prerequisiting targeting to an existing rule or create a new rule with prerequisite targeting. You can specify one or more prerequisite features within the same project and give each a custom evaluation condition. A similar flow exists while editing the targeting rules of an experiment.
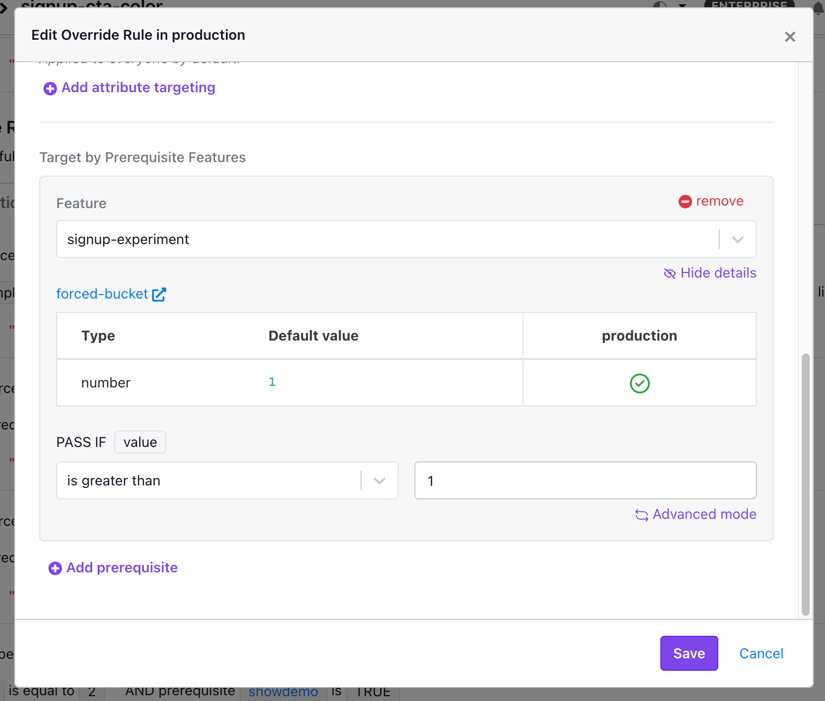
Inline prerequisite states and values
The same deterministic and Schrödinger states apply to inline prerequisites as they do to top-level prerequisites (see above). Below is a summary of how they apply to inline prerequisites:
-
Deterministic states (live and not live) are calculated using your evaluation condition, which is not limited to
is true. As before, no run-time evaluation of prerequisites is required in the SDK.- Live prerequisites which pass the evaluation condition will allow their dependent rules or experiments to be enabled.
- Live prerequisites which fail the evaluation condition will still block their dependent rules or experiments.
- Not live prerequisites will generally block the dependent rule or experiment, unless the evaluation condition specifically checks for this (e.g.
is not live)
-
Schrödinger state prerequisites must be evaluated at runtime in the SDK, and thus a compatible SDK version is required.
Limitations
There are a few limitations and guardrails within GrowthBook when configuring prerequisites:
- Prerequisite features must be in the same project as the dependent feature or experiment.
- You cannot select a prerequisite that would lead to a circular dependency.
- If you don't have an SDK which supports prerequisite evaluation, then you cannot select a prerequisite that is in a Schrödinger state.
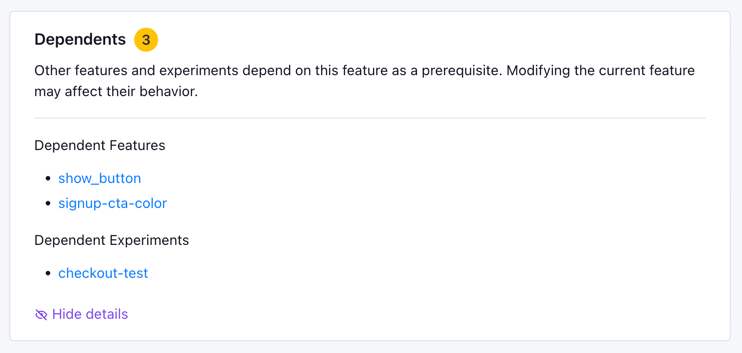
- Once a feature has been used as a prerequisite for other features or experiments, you are blocked from deleting, archiving, or changing its projects. To perform these actions, you must first remove the feature from all dependent features and experiments. You can see a list of dependencies on the feature page: