Official GrowthBook MCP Server
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a standard for integrating AI tools and agents with developer platforms like GrowthBook. This guide shows you how to connect your AI tools to GrowthBook's MCP server and which tools are available for use.
Check us out on the official MCP Registry
Prerequisites
- Node.js: Check if you have it by running
node -v. Install it from nodejs.org - GrowthBook API Key: To create a new key, go to Settings → API Keys → New Secret Key. Use this key in the next step.
Installation
We cover how to connect the GrowthBook MCP server for the most popular tools below, but the installation steps are similar for most AI tools.
Configuration uses the following environment variables:
| Variable Name | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GB_API_KEY | Required | A GrowthBook API key or PAT. When using a PAT, you can only access tools that your permissions allow. |
| GB_EMAIL | Required | Your email address used with GrowthBook. Used when creating feature flags and experiments. |
| GB_API_URL | Optional | Your GrowthBook API URL. Defaults to https://api.growthbook.io. |
| GB_APP_ORIGIN | Optional | Your GrowthBook app URL Defaults to https://app.growthbook.io. |
| GB_HTTP_HEADER* | Optional | Custom HTTP headers included in all API requests. See Custom Headers below. |
You only need to configure GB_API_KEY and GB_EMAIL.
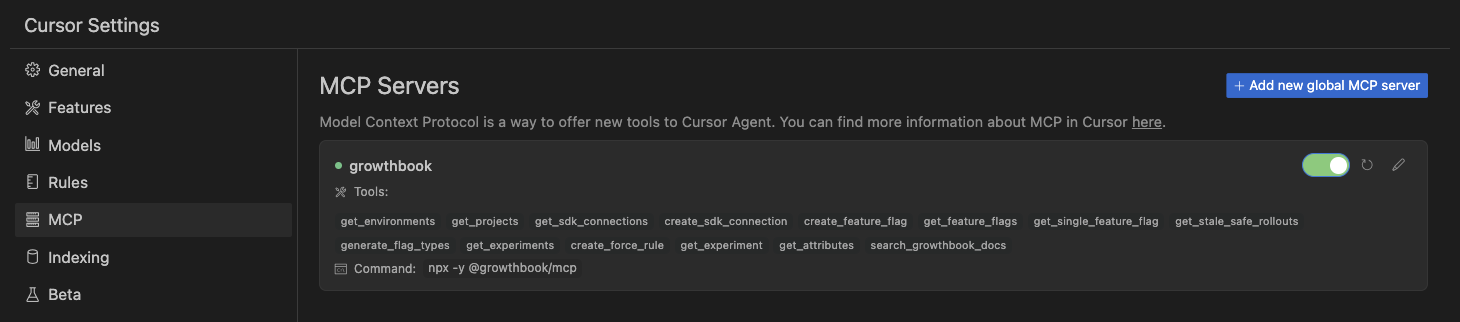
Cursor
- Open Cursor Settings → MCP
- Click Add new global MCP server
- Add an entry for the GrowthBook MCP, following the pattern below:
- macOS
- Windows
- WSL
- Linux
{
"mcpServers": {
"growthbook": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@growthbook/mcp@latest"],
"env": {
"GB_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"GB_API_URL": "YOUR_API_URL",
"GB_APP_ORIGIN": "YOUR_APP_ORIGIN",
"GB_EMAIL": "YOUR_EMAIL"
}
}
}
}
{
"mcpServers": {
"growthbook": {
"command": "cmd",
"args": ["/c", "npx", "-y", "@growthbook/mcp@latest"],
"env": {
"GB_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"GB_API_URL": "YOUR_API_URL",
"GB_APP_ORIGIN": "YOUR_APP_ORIGIN",
"GB_EMAIL": "YOUR_EMAIL"
}
}
}
}
{
"mcpServers": {
"growthbook": {
"command": "wsl",
"args": ["npx", "-y", "@growthbook/mcp@latest"],
"env": {
"GB_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"GB_API_URL": "YOUR_API_URL",
"GB_APP_ORIGIN": "YOUR_APP_ORIGIN",
"GB_EMAIL": "YOUR_EMAIL"
}
}
}
}
{
"mcpServers": {
"growthbook": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@growthbook/mcp@latest"],
"env": {
"GB_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"GB_API_URL": "YOUR_API_URL",
"GB_APP_ORIGIN": "YOUR_APP_ORIGIN",
"GB_EMAIL": "YOUR_EMAIL"
}
}
}
}
- Save the settings.
You should now see a green active status after the server successfully connects!
VS Code
- Open User Settings (JSON)
- Add an MCP entry:
- macOS
- Windows
- WSL
- Linux
{
"servers": {
"growthbook": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@growthbook/mcp@latest"],
"env": {
"GB_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"GB_API_URL": "YOUR_API_URL",
"GB_APP_ORIGIN": "YOUR_APP_ORIGIN",
"GB_EMAIL": "YOUR_EMAIL"
}
}
}
}
{
"servers": {
"growthbook": {
"command": "cmd",
"args": ["/c", "npx", "-y", "@growthbook/mcp@latest"],
"env": {
"GB_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"GB_API_URL": "YOUR_API_URL",
"GB_APP_ORIGIN": "YOUR_APP_ORIGIN",
"GB_EMAIL": "YOUR_EMAIL"
}
}
}
}
{
"servers": {
"growthbook": {
"command": "wsl",
"args": ["npx", "-y", "@growthbook/mcp@latest"],
"env": {
"GB_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"GB_API_URL": "YOUR_API_URL",
"GB_APP_ORIGIN": "YOUR_APP_ORIGIN",
"GB_EMAIL": "YOUR_EMAIL"
}
}
}
}
{
"servers": {
"growthbook": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@growthbook/mcp@latest"],
"env": {
"GB_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"GB_API_URL": "YOUR_API_URL",
"GB_APP_ORIGIN": "YOUR_APP_ORIGIN",
"GB_EMAIL": "YOUR_EMAIL"
}
}
}
}
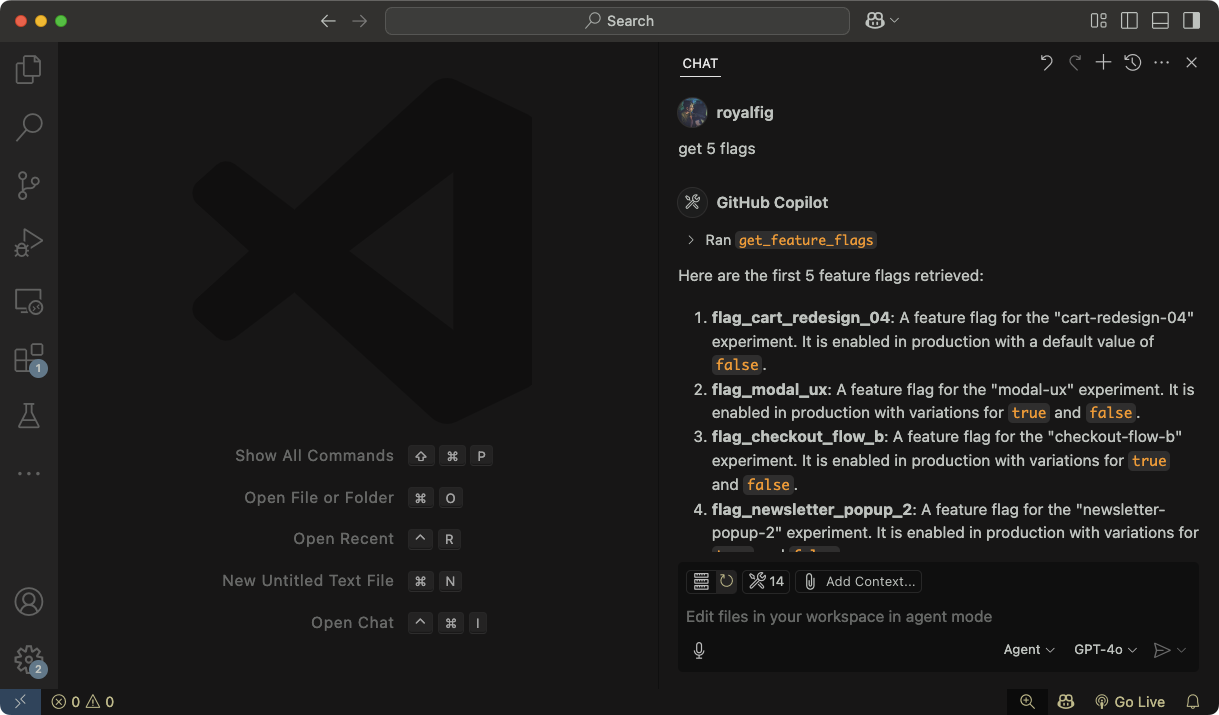
- Save your settings. In your file, a Start button will appear. Click it to the start the server.
In CoPilot Chat, you'll see a tool icon, indicating the server is connected successfully. GrowthBook MCP is now ready to use in VS Code.
Claude Code
Claude Code uses command-line commands to add MCP servers. Run the following command in your terminal:
claude mcp add growthbook --transport stdio --env GB_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEY --env GB_API_URL=YOUR_API_URL --env GB_APP_ORIGIN=YOUR_APP_ORIGIN --env GB_EMAIL=YOUR_EMAIL -- npx -y @growthbook/mcp@latest
All options (--transport, --env, etc.) must come before the server name. The -- (double dash) separates the server name from the command and arguments that get passed to the MCP server.
You can verify the server was added by running:
claude mcp get growthbook
To see all configured MCP servers, use:
claude mcp list
Within Claude Code, you can check server status using the /mcp command.
Claude Desktop
We have an official extension in the Connectors Directory.
- Go to Settings → Extensions → Browse Extensions
- Select Desktop Extensions and search for "GrowthBook"
- Follow the prompts to install and configure the extension
- That's it!
Claude Desktop ships with its own version of Node, which means it's not required here
Custom Headers
If your GrowthBook instance is behind a reverse proxy or requires additional authentication headers (e.g. Cloudflare Access), you can pass custom HTTP headers via environment variables using the GB_HTTP_HEADER_* prefix.
Each environment variable following this pattern is automatically converted to a proper HTTP header and included in every API request the MCP server makes.
Naming Convention
The variable name after the GB_HTTP_HEADER_ prefix is converted from UPPER_SNAKE_CASE to Title-Case-With-Dashes:
| Environment Variable | HTTP Header Sent |
|---|---|
GB_HTTP_HEADER_X_TENANT_ID | X-Tenant-ID |
GB_HTTP_HEADER_CF_ACCESS_TOKEN | Cf-Access-Token |
GB_HTTP_HEADER_X_CUSTOM_AUTH | X-Custom-Auth |
Custom headers cannot override the Authorization or Content-Type headers, which are always set by the MCP server.
Example: Cloudflare Access
If your self-hosted GrowthBook is protected by Cloudflare Access, add the service token headers:
- macOS / Linux
- Windows
{
"mcpServers": {
"growthbook": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@growthbook/mcp@latest"],
"env": {
"GB_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"GB_API_URL": "https://growthbook.internal.example.com",
"GB_APP_ORIGIN": "https://growthbook.internal.example.com",
"GB_EMAIL": "YOUR_EMAIL",
"GB_HTTP_HEADER_CF_ACCESS_CLIENT_ID": "YOUR_CF_CLIENT_ID",
"GB_HTTP_HEADER_CF_ACCESS_CLIENT_SECRET": "YOUR_CF_CLIENT_SECRET"
}
}
}
}
{
"mcpServers": {
"growthbook": {
"command": "cmd",
"args": ["/c", "npx", "-y", "@growthbook/mcp@latest"],
"env": {
"GB_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"GB_API_URL": "https://growthbook.internal.example.com",
"GB_APP_ORIGIN": "https://growthbook.internal.example.com",
"GB_EMAIL": "YOUR_EMAIL",
"GB_HTTP_HEADER_CF_ACCESS_CLIENT_ID": "YOUR_CF_CLIENT_ID",
"GB_HTTP_HEADER_CF_ACCESS_CLIENT_SECRET": "YOUR_CF_CLIENT_SECRET"
}
}
}
}
For Claude Code, append the custom headers as additional --env flags:
claude mcp add growthbook --transport stdio \
--env GB_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEY \
--env GB_API_URL=https://growthbook.internal.example.com \
--env GB_APP_ORIGIN=https://growthbook.internal.example.com \
--env GB_EMAIL=YOUR_EMAIL \
--env GB_HTTP_HEADER_CF_ACCESS_CLIENT_ID=YOUR_CF_CLIENT_ID \
--env GB_HTTP_HEADER_CF_ACCESS_CLIENT_SECRET=YOUR_CF_CLIENT_SECRET \
-- npx -y @growthbook/mcp@latest
Example: Multi-Tenant Proxy
If your API gateway requires a tenant identifier:
"env": {
"GB_API_KEY": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"GB_EMAIL": "YOUR_EMAIL",
"GB_HTTP_HEADER_X_TENANT_ID": "your-tenant-id"
}
You can add as many GB_HTTP_HEADER_* variables as needed — each one becomes a separate header on every request.
Tools
Feature Flags
create_feature_flag: Create, add, or wrap an element with a feature flag. Accepts key, type, default value, and other metadata.get_feature_flags: List feature flags in your GrowthBook instance. Include a feature ID to retrieve a single flag.get_stale_feature_flags: Given a list of feature flag IDs, checks whether each one is stale and returns cleanup guidance including replacement values and SDK search patterns.create_force_rule: Add a targeting condition (e.g.,country = CA) to an existing flag.generate_flag_types: Generate TypeScript types for feature flags.
Experiments
get_experiments: List experiments in GrowthBook. Include an experiment ID to return data about a single experiment.- This tool has 3 modes:
metadata: The default response from the GrowthBook API, including basic information about experiments.full: Metadata about experiments plus results. Warning: This returns a large payload, which fills up the context window quickly.summary: Presents a high-level summary of experiments and their results, combining experiment metadata, results, and metrics.
- This tool has 3 modes:
get_attributes: List user attributes tracked in GrowthBook (useful for targeting).create_experiment: Creates an A/B test. Optionally, provide a feature ID to link the experiment to a feature flag. Note: this tool callsget_defaults, which provides a sampling of previous experiments to help the AI agent create the experiment correctly. For better performance, these defaults are saved to the local file system and periodically updated.get_defaults: Get default values for experiments including hypothesis, description, datasource, and assignment query. (Runs automatically when the create experiment tool is called.)create_defaults: Set custom default values for experiments that will be used when creating new experiments.clear_user_defaults: Clear user-defined defaults and revert to automatic defaults.
Environments
get_environments: List all environments (e.g., production, staging) configured in GrowthBook.
Projects
get_projects: List all projects in your GrowthBook instance.
SDK Connections
get_sdk_connections: List SDK connections (how GrowthBook connects to your apps).create_sdk_connection: Create a new SDK connection for your app, specifying language and environment.
Metrics
get_metrics: List fact and legacy metrics (useful for better understanding experiments). Include a metric ID to return details about a specific metric.
Documentation Search
search_growthbook_docs: Search the GrowthBook documentation for information on how to use a feature, by keyword or question.
Example Prompts
Here are some prompts to try with your AI assistant once the MCP server is connected:
Feature Flags
- "Create a boolean feature flag called
new-checkout-flowthat defaults tofalse" - "Show me the details and rules for the
dark-modefeature flag" - "Add a force rule to
new-checkout-flowthat enables it for users wherecountryisUS" - "Check if these flags are stale and can be cleaned up:
old-banner,beta-pricing,temp-fix" - "Generate TypeScript types for all my feature flags"
Experiments
- "Summarize the results of my last 5 experiments"
- "Create an A/B test on the
new-checkout-flowflag with a control (false) and treatment (true)" - "Show me the full results for experiment
exp_abc123, including metric breakdowns"
General
- "What SDK connections do I have set up?"
- "Search the GrowthBook docs for how to set up a fact metric"
- "List all my projects and environments"
Video Tutorial
Watch this video for a complete walkthrough of setting up and using the GrowthBook MCP Server:
Next steps
Now that you're connected, start using GrowthBook's MCP tools directly from your editor to:
- Add new flags to your code and GrowthBook
- Generate type definitions for your flags for typesafe feature flagging
- Create new feature-flag experiements
- Search the GrowthBooks docs without leaving the editor
- Check out the GrowthBook MCP Server code on GitHub