Data Pipeline Mode
EnterprisePipeline Mode is available on Enterprise plans. Availability differs by warehouse and pipeline strategy.
Pipeline mode will provide substantial savings for experimenters with lots of data and/or long-running experiments. With Pipeline Mode, GrowthBook writes intermediate tables back to your warehouse and re-uses those across metric analyses in an experiment.
Pipeline mode supports two strategies:
- Incremental refresh (Recommended) — On each update, only scans new rows in your experiment assignment and metric sources, and persists reusable intermediate tables across updates to minimize re-scans and speed up analyses.
- Ephemeral (Legacy) — Per-analysis, short-lived tables are created with limited retention for reuse within an analysis window.
Incremental refresh (Recommended, in Beta)
Our main pipeline mode reduces cost and speeds up experiment updates by scanning only new data since the last run, while keeping a small set of reusable, de-duplicated tables in your warehouse.
Incremental refresh is only available for BigQuery and Presto/Trino. Please reach out to support if your warehouse is not supported.
How it works
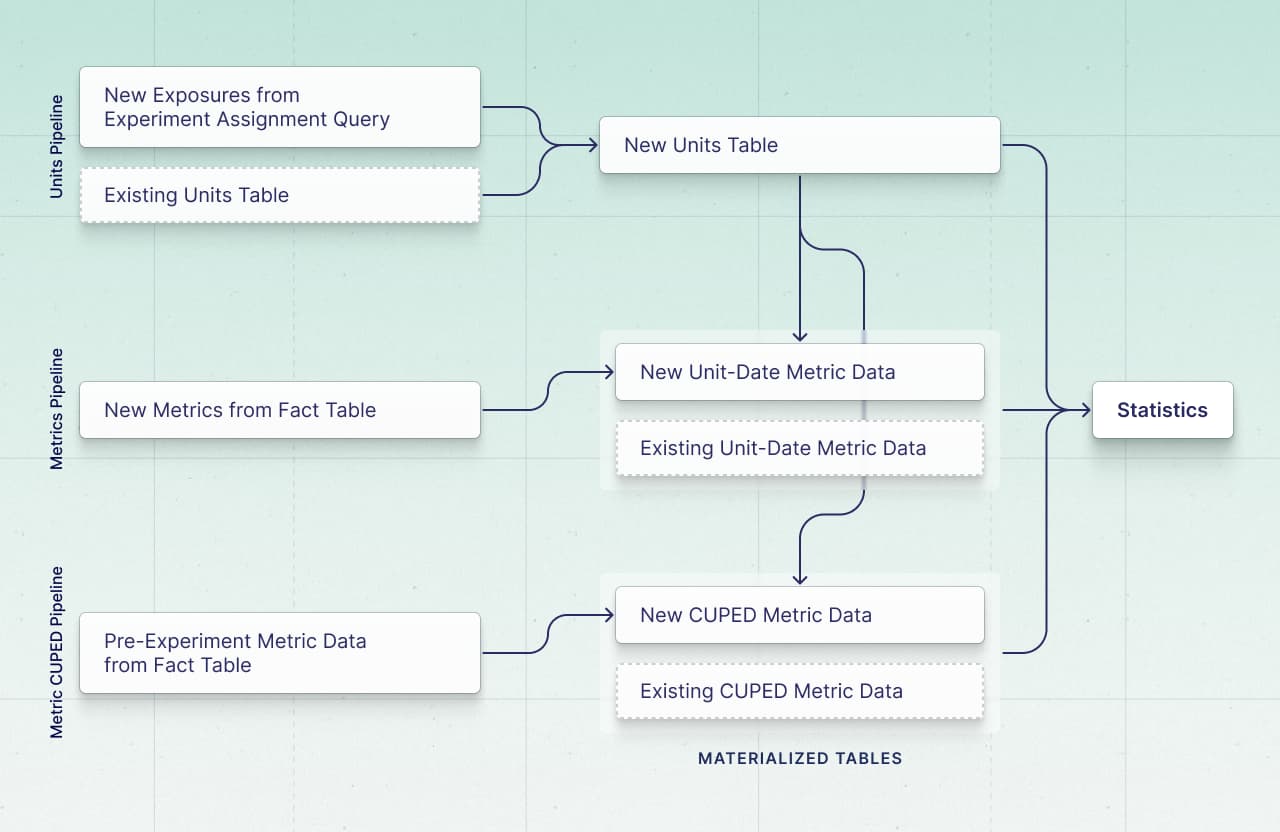
On each experiment update, GrowthBook only scans new data in your warehouse to keep the amount of data consumed to a minimum. Then, GrowthBook materializes several tables in your warehouse to ensure old data does not need to be scanned again, and to reduce the computation needed in future analyses.
Specifically, for the experiment assignment query and fact tables, GrowthBook uses the max timestamp seen in the previous update and only scans for data since that last update, inserting that data into materialized intermediate tables to be used for analysis.
Main benefits
- Dramatic reduction in the number of rows scanned per update, as GrowthBook only has to scan your experiment assignment queries and fact tables for data in partitions that are on or after the last timestamp seen in the previous update.
- Dramatic reduction in the cost and waiting time when running on-demand dimension analyses, as GrowthBook can use the existing materialized tables,
Experiment Units Tableand one or moreUnits-Date Metrics Tableto get dimension breakdowns rather than re-scanning data in your warehouse.
Requirements
- A dedicated schema/dataset with write access for GrowthBook.
- Ability to retain intermediate tables beyond 24 hours (often days) for reuse.
- Appropriate permissions to create/read/update (and when supported, merge/partition) tables.
- Experiment assignment queries and fact tables partitioned on the
timestampcolumn. If you have a different partitioning strategy, please reach out to support.
To see specific instructions for your warehouse, please see the Configuration section below.
Controls and observability
- Default "Update" performs an incremental refresh
- "Full refresh" is available when you need to re-state results (e.g., backfills, config changes)
Limitations and notes
- While in Beta, the following analysis tools aren't supported: activation metrics, quantile metrics, ratio metrics with different numerator and denominator fact tables, and dimension breakdowns in Experiment Dashboards.
- Changes to analysis settings sometimes require a full data refresh to take effect. In the future, we will make improvements to ensure that only the data that need be restated is restated.
- Any changes to fact table sources require using a full refresh to take effect, but we are working on improvements to ensure that only the data that need be restated is restated.
- Exact table schemas and partitioning/retention strategies vary by warehouse.
Enable Incremental refresh
- In your Data Source, open "Data Pipeline Settings"
- Enable Pipeline Mode and select the strategy: "Incremental refresh (Recommended)"
- Set a destination schema/dataset for intermediate tables and choose retention settings
- Save
You can test incremental refresh by enabling it only for a single experiment in the Data Pipeline Settings UI. We do not apply it to old experiments in the case that they have incompatible settings. To confirm pipeline mode is being used, you can look at the queries run for your experiment and validate that they are creating intermediate tables.
Additional technical details
On each incremental update, GrowthBook:
- Scans the experiment assignment source for any new rows that have a timestamp greater than the max timestamp seen on the previous run and updates a de-duplicated units table (one row per unit with timestamps and experiment dimensions).
- Scans each metric's fact source for any new rows that have a timestamp greater than the max timestamp seen on the previous run and updates pre-aggregated metric tables (one row per unit-date-refresh with timestamps and metric dimensions).
- Optionally loads pre-experiment windows for CUPED into a separate table for only newly seen units.
- Joins the above to produce summary statistics and per-dimension breakdowns.
Therefore, GrowthBook will materialize the following tables per experiment:
- The units table (
Experiment Units Table- namedgb_units_<experiment_id>in your warehouse)- one row per unit in the experiment with the unit id, variation id, first exposure timestamp, and experiment dimensions
- this table is joined to new exposures, de-duped, and then re-created on each update
- One or more metrics tables depending on the number of metric sources and the number of metrics (
Unit-Date Metrics Table- namedgb_metrics_<experiment_id>_<metric_source_id>_<random_id>in your warehouse)- one row per unit-date-refresh, as we take new metric values and aggregate them by unit and date on each refresh and insert them into the metrics table
- we insert new rows into this table on each update
- An additional table per above metric source for CUPED (
CUPED Metrics Table- namedgb_cuped_<experiment_id>_<metric_source_id>_<random_id>_covariatein your warehouse)- one row per unit, as we scan the metric source for the pre-experiment window, join it to only new units found in the units update, and then insert the aggregated values per unit into the CUPED table
- we insert new rows into this table on each update
On each update, we look for new rows in your sources. We define "new" rows as those where the row has a timestamp greater than the max timestamp seen on the previous run. This means that if any data is re-stated in your warehouse, or new rows land that are linked to old timestamps, GrowthBook may miss this data unless you do a full refresh. In other words, as data lands, it must have a later timestamp than the data as of the last update or it will not be included in the analysis. This also means that if a Fact Table or Experiment Assignment Table definition includes references to multiple source tables, these tables should be updated at the same time to ensure GrowthBook can capture all data.
GrowthBook is building functionality to support additional use cases, improve control over intermediate table retention, and support additional data sources. Please reach out to support if you have any concerns or questions.
Configuration
While Pipeline mode requires you to give write permissions to your Data Source, GrowthBook only uses it for the Pipeline Mode. All other user-provided SQL statements are validated to be read-only before being executed.
BigQuery
- (strongly recommended, but optional) Create a dedicated dataset to which GrowthBook will write tables. This will keep your data warehouse clean and ensure that we are only writing to a dedicated space.
- Grant permissions to create tables to the role connecting GrowthBook to your warehouse. You can do this by granting your GrowthBook Service Account the
BigQuery Data Editorrole on the new dataset. You can also give only BigQuery table reading and writing permissions on that dataset if you want to be more restrictive. - Navigate to your BigQuery Data Source in GrowthBook and scroll down to "Data Pipeline Settings"
- Click "Edit" and enable pipeline mode, set the destination dataset to your new dedicated GrowthBook dataset from step 1.
Snowflake (Ephemeral only)
- (strongly recommended, but optional) Create a dedicated schema to which GrowthBook will write temporary tables. This will keep your data warehouse clean and ensure that we are only writing to a dedicated space.
- Grant permissions to create tables to the role connecting GrowthBook to your warehouse. The Snowflake role attached to GrowthBook will need
CREATE TABLE,SELECT - FUTURE TABLE, andUSAGEon the schema created in step 1. - Navigate to your Snowflake Data Source in GrowthBook and scroll down to "Data Pipeline Settings"
- Click "Edit" and enable pipeline mode, set the destination schema to your new dedicated GrowthBook schema from step 1, and set the number of hours you will retain our temporary tables. For Snowflake, we recommend leaving the value at 24 as Snowflake's retention is set in days and we will round up to the nearest day.
Databricks (Ephemeral only)
Databricks works slightly differently. Instead of creating a temporary table, we create a regular table for the deduped units assignment and then DROP that table when analysis is completed.
Using pipeline mode in Databricks requires either granting DROP permissions to the Databricks account that GrowthBook uses, or leaving many tables in your schema you have to manually delete later! For this reason we strongly recommend a standalone schema for GrowthBook to use to write tables to.
- (strongly recommended, but optional) Create a dedicated schema to which GrowthBook will write temporary tables. This will keep your data warehouse clean and ensure that we are only writing to and dropping from a dedicated space.
- Grant permissions to your user account or service principal that already has read permission in your warehouse. That user/service principle will need to be able to
USE SCHEMA,CREATE TABLE,DROP TABLE, and toSELECTandEXECUTEin the schema. - Navigate to your Databricks Data Source in GrowthBook and scroll down to "Data Pipeline Settings"
- Click "Edit" and enable pipeline mode, set the destination schema to your new dedicated GrowthBook schema from step 1, and whether you want the table to be deleted (we recommend you leave this setting on as we will not re-use these tables at a later date). If this setting is off, you'll need to manually delete the tables that GrowthBook creates.